The Information Content of an FID
The free induction decay (FID) is a function representing the decay of transverse magnetization as a function of time after the application of a pulse (or pulse sequence). The NMR spectrum is obtained by Fourier transforming the FID. All of the information in the NMR spectrum (line width, intensity, phase, line shape ....) is contained in the FID. Knowledge of what part of the FID represents a particular property of an NMR spectrum allows a user to process the raw time domain data in a way that maximizes the quality and information content of the processed frequency domain spectrum. The figure below shows the real component of the complex FID for a sample in which there is a single resonance. The FID is labelled in terms of its information content.
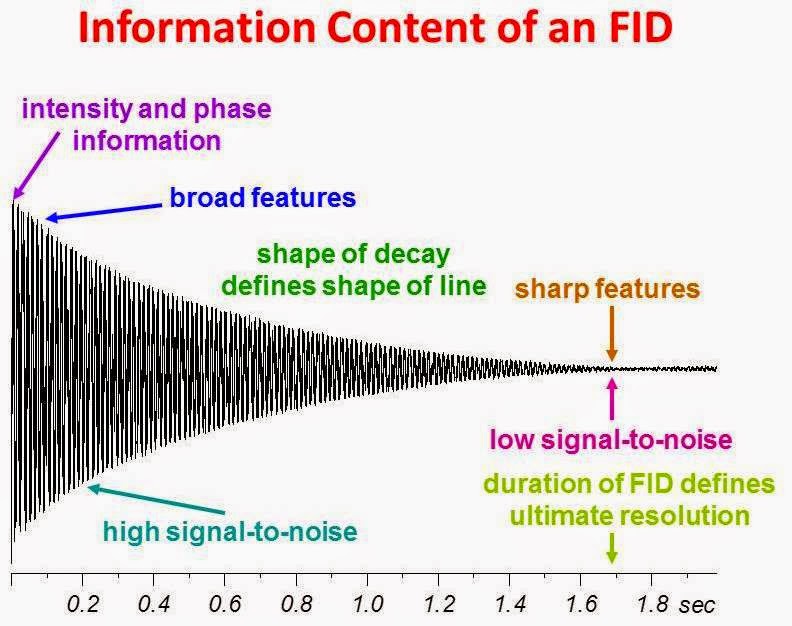
The shape of the envelope of the overall decay defines the line shape of the NMR resonance. Exponential decays yield Lorentzian line shapes. The frequency in the FID represents the offset of the resonance from the carrier frequency or in other words, how far the resonance is from the center of the spectrum. The higher the frequency, the further off-resonance the peak. The FID for an on-resonance peak is a simple decaying exponential with no oscillation frequency present. The first point of the FID contains the integrated intensity and
phase information. Since time and frequency are reciprocals of one another, the duration of the decay before it disappears into the noise determines the sharpness of the NMR resonances and ultimately the resolution in cases where there is more than one resonance in the spectrum. The longer the decay - the narrower the lines. The early portion of the FID (short time) defines the broad features (wide frequency distributions) whereas the the latter portion of the FID (long time) defines the sharp features (narrow frequency distributions). Also, since the FID is a decaying function, the early portion has a higher signal-to-noise ratio than the latter portion. With this knowledge its is very easy to understand how best to apply apodization functions to the raw data for the purpose
line broadening and
resolution enhancement. Processing techniques such as
zero filling,
forward linear prediction,
backward linear prediction and
signal-to-noise optimization as well as spectral artifacts such as
truncation errors,
baseline roll and
receiver saturation errors are easily understood with knowledge of the information content in the FID.


Source:
University of Ottawa NMR Facility Blog


